Hi, I’m Spencer! I’ve dedicated my life to food and education around food systems. I established this website in 2016, designed to encourage and educate people to grow their own staple foods in the tropics. This website was originally devoted to perennial vegetables, but over time my focus has shifted from growing food to growing ecosystems. After living on a highly degraded site, I understood the importance of creating an ecosystem in order to get food plants to flourish. This pushed me into successional agroforestry and syntropic agriculture.

Perennial Vegetables
Be sure to check out the perennial vegetable section of this website featuring plant profiles of tropical perennial vegetables and information and tips on growing them.

Agroforestry
If you’re inspired by growing ecosystems, check out my page on agroforestry and my Youtube account focused on my current project.
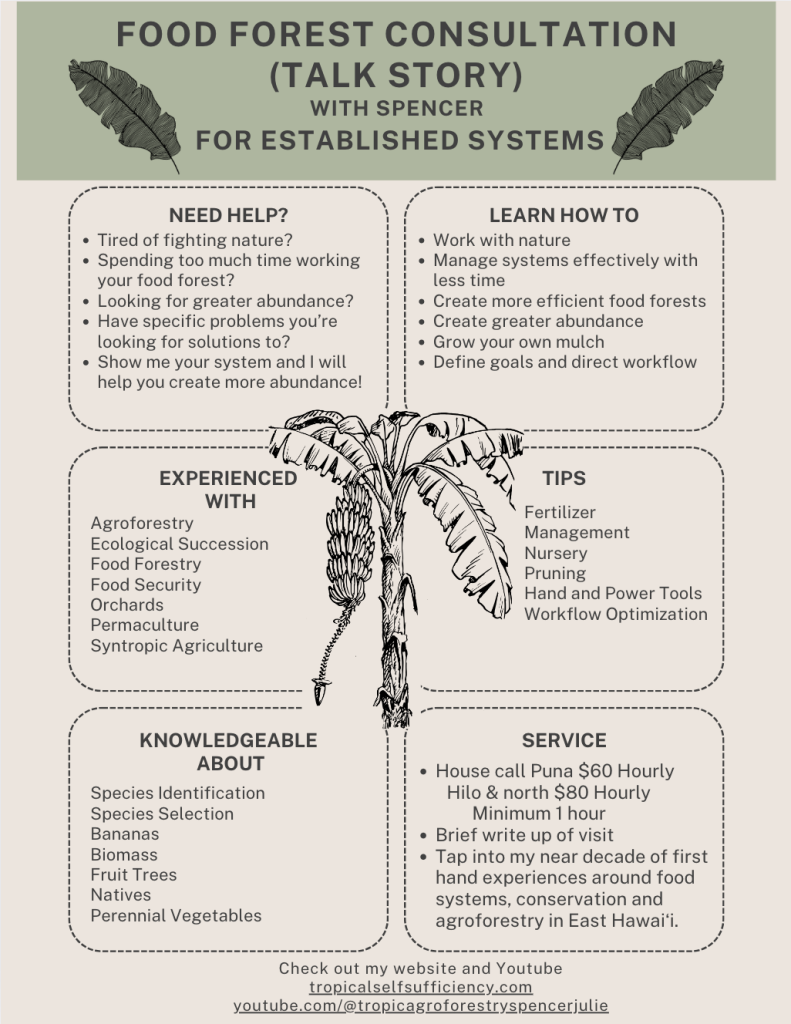
Consultations
If you’re on Big Island East Side and looking for some extra help, I do consultations! I have two types of consultations I perform. One centers around already established food forests, where I come to your site and give you tips and tricks to make your system more efficient and productive. The second type of consultation is for starting a syntropic agroforest from scratch. Please check out my consultation page!